Shows
The Science DevUnlocking the Secrets of Magnetism: New Insights into Exotic Particles in Ultrathin Materialshttps://thescience.dev/unlocking-the-secrets-of-magnetism-new-insights-into-exotic-particles-in-ultrathin-materials/
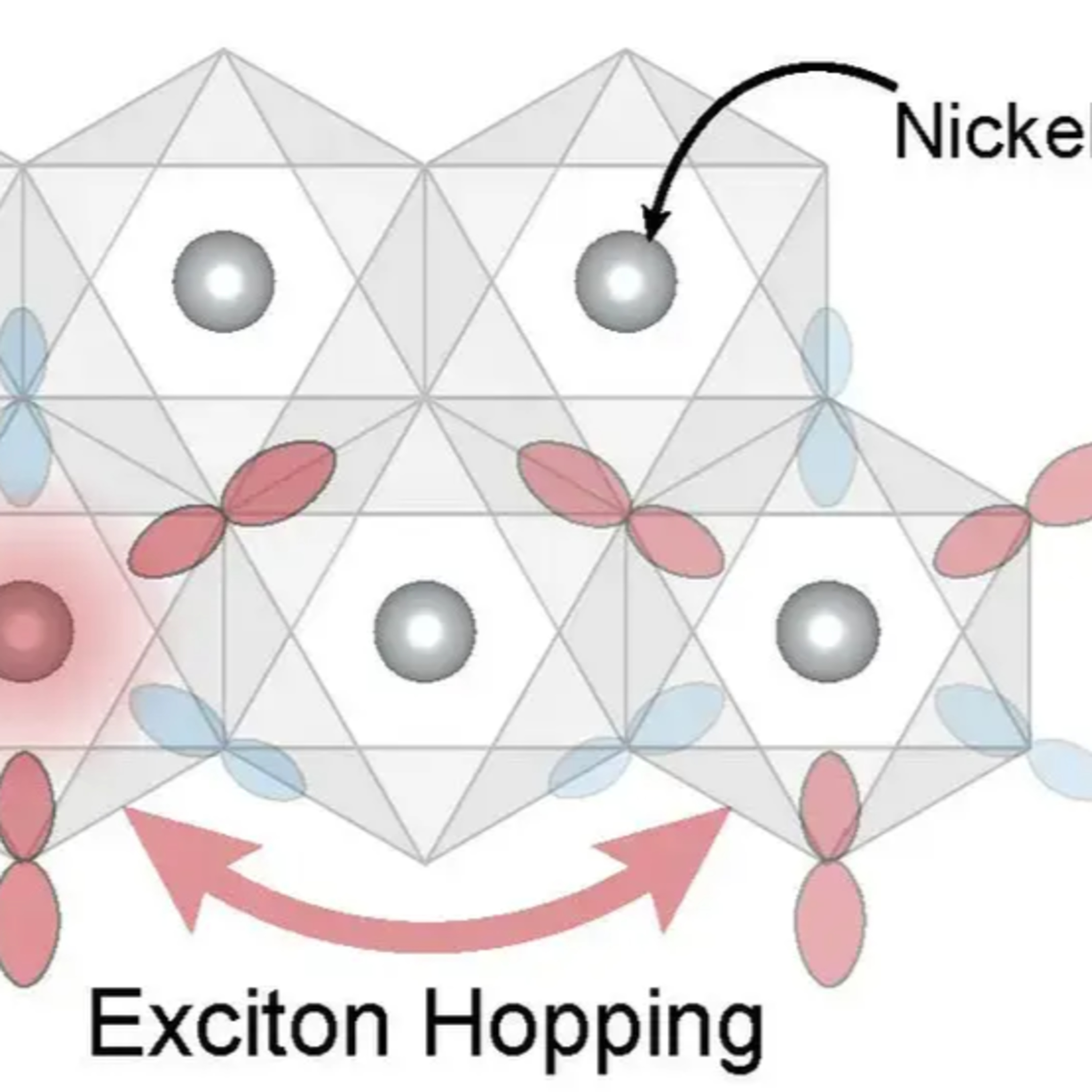
MIT physicists and colleagues have made significant strides in understanding exotic particles called excitons, which play a crucial role in a unique form of magnetism found in ultrathin materials. Their research, utilizing a powerful instrument at Brookhaven National Laboratory, sheds light on the origin, control, and behavior of these particles, paving the way for advancements in electronics and beyond.
2024-09-2910 min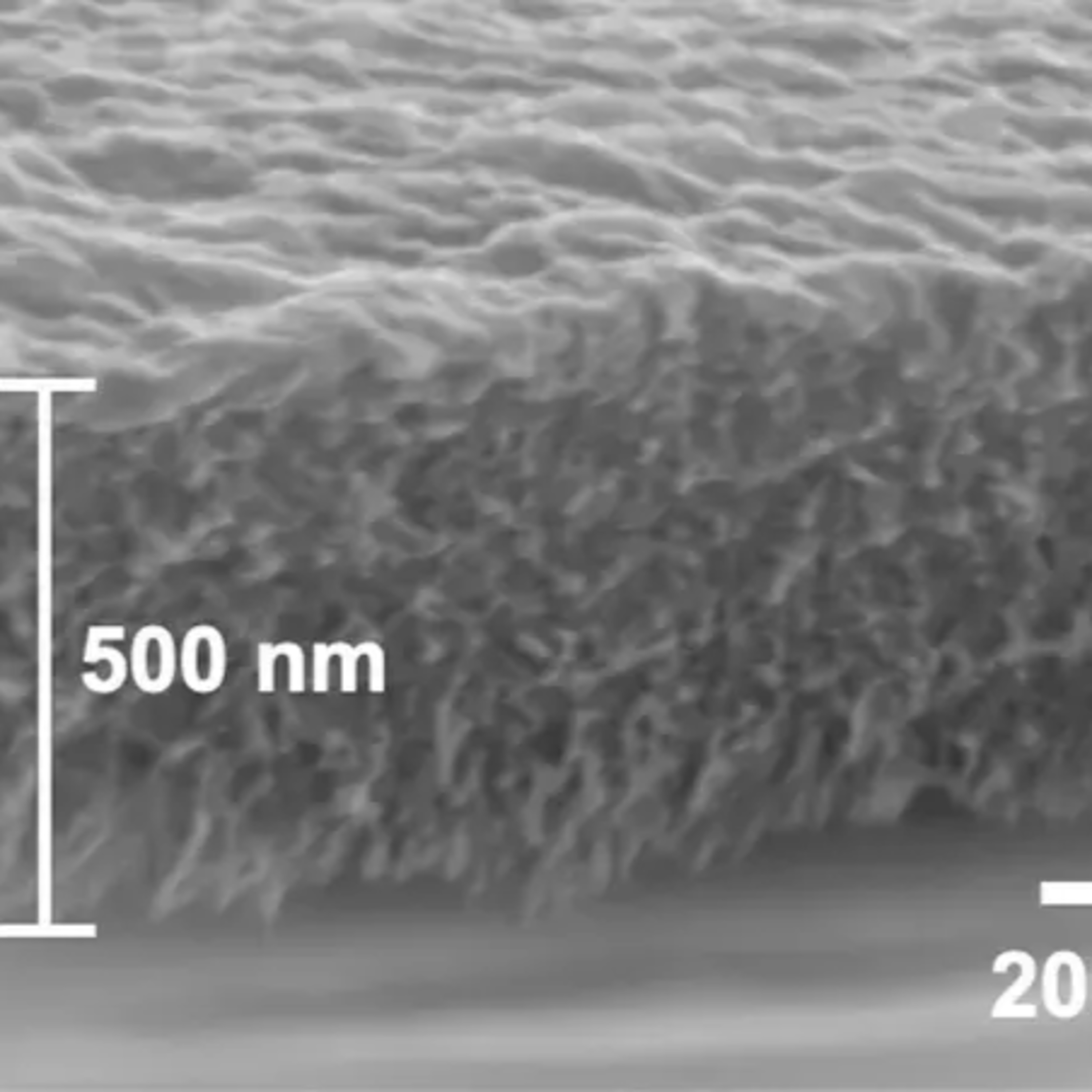
The Science DevA Natural Solution for Forever Chemicals - New Filtration Material Offers Hope for Clean Waterhttps://thescience.dev/a-natural-solution-for-forever-chemicals-new-filtration-material-offers-hope-for-clean-water/
MIT researchers have developed a new filtration material using silk and cellulose that effectively removes persistent chemicals, including PFAS, and heavy metals from water. This nature-based solution also boasts antimicrobial properties, combating the common issue of filter fouling.
2024-09-2906 min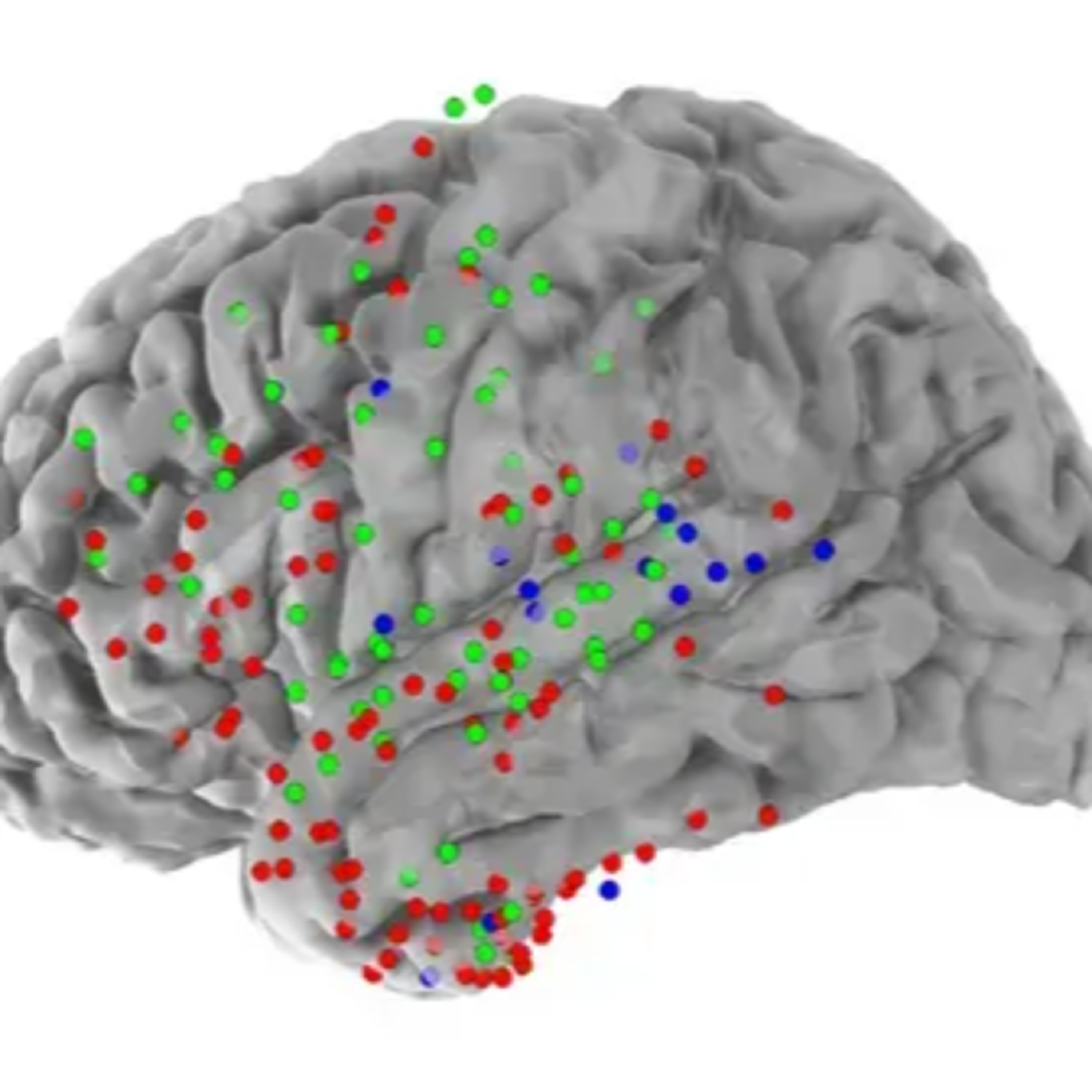
The Science DevNeurons Process Words on Different Timescaleshttps://thescience.dev/neurons-process-words-on-different-timescales/
MIT neuroscientists have discovered distinct groups of neurons within the brain’s language processing centers that operate on different timescales, potentially explaining how we understand both individual words and their combined meaning in sentences.
2024-09-2905 min
The Science DevPhysicists Capture First Images of Frictionless Flow in Ultracold Atomshttps://thescience.dev/physicists-capture-first-images-of-frictionless-flow-in-ultracold-atoms/
MIT physicists have directly observed edge states in a cloud of ultracold atoms, capturing images of atoms flowing along a boundary without resistance. The results could help physicists manipulate electrons to flow without friction in materials, enabling super-efficient, lossless transmission of energy and data.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevNanostructures Enable On-Chip Lightwave-Electronic Frequency Mixerhttps://thescience.dev/nanostructures-enable-on-chip-lightwave-electronic-frequency-mixer/
MIT researchers have developed a lightwave-electronic frequency mixer that operates at petahertz frequencies, enabling the possibility of faster communication technologies and advancements in ultrafast signal processing.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevThe Secret to Dinosaur Collagen’s Longevity Unveiledhttps://thescience.dev/the-secret-to-dinosaur-collagens-longevity-unveiled/
MIT chemists may have cracked the code of collagen’s incredible longevity, a puzzle that has intrigued scientists studying dinosaur fossils. Their research points to a unique atomic-level interaction that shields collagen from degradation, potentially explaining its survival over millions of years.
2024-09-2905 min
The Science DevToward a Code-Breaking Quantum Computerhttps://thescience.dev/toward-a-code-breaking-quantum-computer/
MIT researchers have developed a new quantum algorithm that could bring us one step closer to breaking the encryption that protects our online communications.
2024-09-2911 min
The Science DevA Battery Breakthrough: Disordered Rock Salts for Sustainable Energy Storagehttps://thescience.dev/a-battery-breakthrough-disordered-rock-salts-for-sustainable-energy-storage/
Researchers at MIT have made a significant breakthrough in battery technology with a new cathode material that promises high energy density, improved stability, and lower cost. This innovation could revolutionize energy storage for everything from electric vehicles to renewable energy grids.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevFasting’s Double-Edged Sword: Regeneration Boost and Cancer Riskhttps://thescience.dev/fastings-double-edged-sword-regeneration-boost-and-cancer-risk/
New research from MIT reveals that while fasting can enhance the regenerative abilities of intestinal stem cells, this benefit comes with a potential downside: an increased risk of tumor development if cancer-causing mutations occur during the refeeding period.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevRevolutionizing Wind Power: A New Theory for Rotor Aerodynamicshttps://thescience.dev/revolutionizing-wind-power-a-new-theory-for-rotor-aerodynamics/
For over a century, the design and operation of wind turbines have relied on aerodynamic principles that often fall short in real-world scenarios. Now, MIT engineers have developed a groundbreaking physics-based model that accurately predicts airflow around rotors, paving the way for significant improvements in wind farm efficiency and energy output.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevPromising Signs of Water Found in Ancient Martian Rockshttps://thescience.dev/promising-signs-of-water-found-in-ancient-martian-rocks/
Scientists have discovered evidence of water in rock samples collected from Mars’ Jezero Crater, suggesting a once habitable environment. These findings, published in AGU Advances, stem from the analysis of seven samples retrieved by NASA’s Perseverance rover.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevNew Open-Source Tool Helps to Detangle the BrainResearchers have developed NeuroTrALE, an open-source software pipeline that uses machine learning and supercomputing to automate the processing and annotation of brain imaging data, accelerating the creation of detailed brain atlases.
https://thescience.dev/new-open-source-tool-helps-to-detangle-the-brain/
2024-09-2911 min
The Science DevImplantable Sensor Offers Hope in Fight Against Opioid Over doseIn a breakthrough development, researchers at MIT and Brigham and Women’s Hospital have engineered an implantable sensor capable of detecting an opioid overdose and automatically delivering a life-saving dose of naloxone. This innovative device, approximately the size of a stick of gum, promises a new line of defense for those most vulnerable to the ongoing opioid crisis.
https://thescience.dev/implantable-sensor-offers-hope-in-fight-against-opioid-overdose/
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevTuning in to Brain Health: How 40Hz Sensory Stimulation May Preserve MyelinNew research from MIT delves into the mechanisms by which 40Hz sensory stimulation may protect myelin, the crucial fatty insulation surrounding nerve fibers in the brain. The study, conducted on a mouse model of myelin loss, offers hope for potential treatments for Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological conditions.
https://thescience.dev/tuning-in-to-brain-health-how-40hz-sensory-stimulation-may-preserve-myelin/
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevFine-Tuning Quantum Materials: A New Approach Using Hydrogen Ionshttps://thescience.dev/fine-tuning-quantum-materials-a-new-approach-using-hydrogen-ions/
Researchers at MIT have developed a new, ultra-precise method for fine-tuning the properties of quantum materials. This technique, which involves bombarding the material with hydrogen ions, could lead to significant advancements in superconductivity, thermoelectric materials, and quantum computing.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevSimPLE Pick-and-Place: A New Model for Precision in Roboticshttps://thescience.dev/simple-pick-and-place-a-new-model-for-precision-in-robotics/
A new study from MIT researchers introduces SimPLE, a novel approach to robotic pick-and-place that leverages simulation and visuotactile sensing to achieve high precision without task-specific training. This breakthrough promises more flexible and adaptable robotic solutions for a variety of industries.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevHelping Robots Practice Skills Independently to Adapt to Unfamiliar Environmentshttps://thescience.dev/helping-robots-practice-skills-independently-to-adapt-to-unfamiliar-environments/
A new algorithm from MIT’s CSAIL and The AI Institute allows robots to practice skills autonomously, potentially leading to more adaptable machines in various settings.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevNew Flexible Electronics Material Offers Hope of Combating E-Wastehttps://thescience.dev/new-flexible-electronics-material-offers-hope-of-combating-e-waste/
A novel flexible substrate material developed through a collaboration between MIT, the University of Utah, and Meta promises to revolutionize the electronics industry by enabling both the recycling of materials and the production of more complex circuitry.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevThe Moon’s Whisper-Thin Atmosphere: A Tale Written in Meteorite Dusthttps://thescience.dev/the-moons-whisper-thin-atmosphere-a-tale-written-in-meteorite-dust/
While the moon lacks any breathable air, it does host a barely-there atmosphere. New research reveals that this delicate atmosphere is primarily a product of impact vaporization, a process where meteorites and micrometeoroids continuously bombard the lunar surface, vaporizing atoms and lofting them into the air.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevA Human Fingerprint on the Sky: Scientists Link Rising Upper Troposphere Ozone to Human Activityhttps://thescience.dev/a-human-fingerprint-on-the-sky-scientists-link-rising-upper-troposphere-ozone-to-human-activity/
New research from MIT confirms that the rising levels of ozone in the upper troposphere, a trend with significant implications for global warming, are largely attributable to human activities. This finding paves the way for targeted strategies to mitigate ozone’s impact on the climate.
2024-09-2904 min
The Science DevA New Era of Blood Pressure Management: Real-Time Insights for Critical Carehttps://thescience.dev/a-new-era-of-blood-pressure-management-real-time-insights-for-critical-care/
A groundbreaking mathematical model, developed at MIT, promises to revolutionize blood pressure management in critical care settings. By accurately and rapidly estimating cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance, the two key determinants of blood pressure, this innovation empowers medical professionals to make more informed treatment decisions in real time.
2024-09-2905 min
The Science DevA New Era in Electronics? Ultrathin Transistor Shows Remarkable Promisehttps://thescience.dev/a-new-era-in-electronics-ultrathin-transistor-shows-remarkable-promise/
Researchers at MIT have developed a new transistor using an ultrathin ferroelectric material, demonstrating properties that could revolutionize electronics. This breakthrough could lead to faster, more durable, and energy-efficient devices, impacting everything from computer memory to energy storage.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevA Recipe for Zero-Emission Fuel: Soda Cans, Seawater, and Caffeinehttps://thescience.dev/a-recipe-for-zero-emission-fuel-soda-cans-seawater-and-caffeine/
MIT engineers have discovered a novel method for producing hydrogen fuel using recycled aluminum, seawater, and a touch of caffeine. This breakthrough could pave the way for sustainable and readily available clean energy, particularly for marine applications.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevStudy Across Multiple Brain Regions Identifies Alzheimer’s Vulnerability and Resilience Factorshttps://thescience.dev/study-across-multiple-brain-regions-identifies-alzheimers-vulnerability-and-resilience-factors/
A new MIT study published in Nature provides compelling evidence for how specific cells and circuits become vulnerable in Alzheimer’s disease. The research also sheds light on factors that may contribute to cognitive resilience in some individuals, even in the presence of disease pathology.
2024-09-2911 min
The Science DevProton Power: Unlocking Green Energy with New Materialshttps://thescience.dev/proton-power-unlocking-green-energy-with-new-materials/
MIT engineers have identified key traits of materials that could lead to the development of highly efficient proton conductors, paving the way for greener energy technologies like fuel cells and hydrogen production.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevThe Human Factor: Why Large Language Models Fail to Meet Our Expectationshttps://thescience.dev/the-human-factor-why-large-language-models-fail-to-meet-our-expectations/
New research from MIT reveals a critical misalignment between how humans perceive the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) and how these models actually perform, potentially leading to overreliance and unexpected failures.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevAI Model Predicts Progression of Breast Tumors to Invasive Cancerhttps://thescience.dev/ai-model-predicts-progression-of-breast-tumors-to-invasive-cancer/
A new AI model developed by researchers at MIT and ETH Zurich can identify different stages of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) from a simple breast tissue image, potentially streamlining diagnosis and reducing overtreatment.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevA Planetary Tango: Astronomers Observe a Hot Jupiter in the Makinghttps://thescience.dev/a-planetary-tango-astronomers-observe-a-hot-jupiter-in-the-making/
A newly discovered planet, TIC 241249530b, is captivating astronomers with its wild, elongated orbit. This “juvenile planet”, on its way to becoming a scorching hot Jupiter, offers a glimpse into the dramatic evolution of these extreme celestial bodies.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevAI Predicts Material Thermal Properties at Lightning Speedhttps://thescience.dev/ai-predicts-material-thermal-properties-at-lightning-speed/
A groundbreaking machine-learning framework developed by researchers at MIT and other institutions can predict how heat moves through materials up to 1,000 times faster than existing AI methods. This advancement could lead to significantly more efficient power generation systems and faster micro electronics.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevHow Anesthesia Drug Propofol Disrupts Brain’s Balance to Induce Unconsciousnesshttps://thescience.dev/how-anesthesia-drug-propofol-disrupts-brains-balance-to-induce-unconsciousness/
MIT neuroscientists have discovered how the common anesthesia drug propofol induces unconsciousness, revealing its disruption of the brain’s balance between stability and excitability. This finding could lead to better tools for monitoring patients under general anesthesia.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevWhen to trust an AI modelhttps://thescience.dev/when-to-trust-an-ai-model/
MIT researchers have developed a new technique, called IF-COMP, that improves the accuracy and efficiency of uncertainty estimations in machine learning models. This breakthrough could help users, especially those without machine learning expertise, better understand when to trust an AI’s predictions.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevSun-Like Stars Found Orbiting Hidden Companionshttps://thescience.dev/sun-like-stars-found-orbiting-hidden-companions/
Most stars in our universe come in pairs. While our own Sun is a loner, many stars like our Sun orbit similar stars, while a host of other exotic pairings between stars and cosmic orbs pepper the universe. Black holes, for example, are often found orbiting each other. One pairing that has proved to be quite rare is that between a Sun-like star and a type of dead star called a neutron star.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevNew Computer Vision Method Accelerates Electronic Material Screeninghttps://thescience.dev/new-computer-vision-method-accelerates-electronic-material-screening/
MIT engineers have developed a groundbreaking computer vision technique that significantly accelerates the characterization of newly synthesized electronic materials, potentially revolutionizing the development of next-generation solar cells, transistors, and LEDs.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevNew Algorithm Discovers Language Just by Watching Videoshttps://thescience.dev/new-algorithm-discovers-language-just-by-watching-videos/
A new algorithm called DenseAV, developed by researchers at MIT learns languages by watching videos.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevJust Thinking About a Location Activates Mental Maps in the Brainhttps://thescience.dev/just-thinking-about-a-location-activates-mental-maps-in-the-brain/
New research from MIT has found that mental maps typically used for navigation, are also created and activated when you merely think about sequences of experiences, even without physical movement or sensory input.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevA Smarter Way to Streamline Drug Discoveryhttps://thescience.dev/a-smarter-way-to-streamline-drug-discovery/
MIT researchers developed an algorithmic framework to automatically identify optimal molecular candidates for drug discovery, minimizing synthetic cost while maximizing the likelihood candidates have desired properties.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevAre Waves Shaping Titan’s Lakes? MIT Study Suggests They Might Behttps://thescience.dev/are-waves-shaping-titans-lakes-mit-study-suggests-they-might-be/
New research from MIT suggests that waves may be responsible for shaping the shorelines of Titan’s lakes and seas. By modeling different erosion processes, scientists found that wave action best explained the observed features, offering a glimpse into the dynamic nature of this intriguing moon.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevCHARMed: A New Hope for Fatal Prion Diseaseshttps://thescience.dev/charmed-a-new-hope-for-fatal-prion-diseases/
In a race against time, researchers at the Broad Institute and Whitehead Institute have developed CHARM, a promising new gene therapy tool that could silence disease-causing genes, offering hope for patients with fatal prion diseases and other genetic conditions.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevPredicting the Unpredictable: Computational Modeling Guides Azetidine Synthesishttps://thescience.dev/predicting-the-unpredictable-computational-modeling-guides-azetidine-synthesis/
Using this new approach, researchers could develop drug compounds with unique pharmaceutical properties.
2024-09-2911 min
The Science DevAI’s Demographic Shortcuts Lead to Diagnostic Bias in Medical Image Analysishttps://thescience.dev/ais-demographic-shortcuts-lead-to-diagnostic-bias-in-medical-image-analysis/
A new MIT study reveals that AI models used to analyze medical images, while highly accurate overall, often exhibit significant bias, performing worse on women and people of color. The research suggests these models may be taking demographic shortcuts, leading to inaccurate diagnoses for certain groups.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevA Natural Gait: Prosthesis Driven by Nervous System Allows for Near-Natural Walkinghttps://thescience.dev/a-natural-gait-prosthesis-driven-by-nervous-system-allows-for-near-natural-walking/
MIT researchers, in collaboration with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, have developed a new surgical technique and neuroprosthetic interface that allows for a prosthetic leg to be fully controlled by the body’s nervous system, leading to a more natural walking gait for amputees.
2024-09-2912 min
The Science DevScientists Achieve Record-Setting Electron Mobility in New Crystal Filmhttps://thescience.dev/scientists-achieve-record-setting-electron-mobility-in-new-crystal-film/
Physicists at MIT, the Army Research Lab, and elsewhere have achieved a record-setting level of electron mobility in a thin film of ternary tetradymite, a mineral with potential applications in electronics and spintronics.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevImplantable Microphone for Fully Internal Cochlear Implantshttps://thescience.dev/implantable-microphone-for-fully-internal-cochlear-implants/
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking implantable microphone, the UmboMic, that could revolutionize cochlear implants by eliminating the need for external hardware. This tiny device, designed to sense minute vibrations in the middle ear, offers hope for a future where cochlear implants are fully internalized, enhancing user experience and expanding access to this life-changing technology.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevMIT Researchers Forge Path to Stronger Titanium Alloyshttps://thescience.dev/mit-researchers-forge-path-to-stronger-titanium-alloys/
MIT researchers, in collaboration with ATI Specialty Materials, have devised a novel approach to enhance the strength and ductility of titanium alloys, potentially revolutionizing industries from aerospace to biomedicine.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevHow to Increase Plastic Recycling Rates in the U.S.https://thescience.dev/how-to-increase-plastic-recycling-rates-in-the-u-s/
While recycling systems and bottle deposits are becoming more common in the U.S., the actual rates of plastic recycling remain disappointingly low. A new study by MIT researchers explores the reasons behind this discrepancy and offers potential solutions for a more sustainable future.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevMicrobe Superheroes: MIT Engineers Develop Method to Protect Beneficial Bacteria from Extreme Conditionshttps://thescience.dev/microbe-superheroes-mit-engineers-develop-method-to-protect-beneficial-bacteria-from-extreme-conditions/
MIT engineers have developed a groundbreaking method to enhance the resilience of beneficial microbes, enabling them to withstand extreme conditions like those found in space and industrial processing. This innovation holds immense potential for applications ranging from space exploration to human health and agriculture.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevThe Ocean’s Carbon Storage Capacity May Be Overestimatedhttps://thescience.dev/the-oceans-carbon-storage-capacity-may-be-overestimated/
A new MIT study reveals that a weakening ocean circulation, a consequence of climate change, could lead to increased carbon dioxide release from the deep ocean into the atmosphere, challenging previous assumptions about the ocean’s role as a carbon sink.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevExotic Black Holes Could Be a Byproduct of Dark Matterhttps://thescience.dev/exotic-black-holes-could-be-a-byproduct-of-dark-matter/
MIT physicists have found that the primordial processes that may have formed dark matter would also have produced even smaller black holes with unprecedented amounts of a nuclear physics property known as “color charge.”
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevDeciphering the Genome’s Control Panel: New Technique Maps Gene-Enhancer Interactionshttps://thescience.dev/deciphering-the-genomes-control-panel-new-technique-maps-gene-enhancer-interactions/
MIT researchers have developed a novel technique to observe the intricate timing of gene and enhancer activation within a cell, offering a powerful tool for understanding gene regulation and its implications for disease.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevA Hair-Thin Hope: Ultrasound Offers New Path for Deep Brain Stimulationhttps://thescience.dev/a-hair-thin-hope-ultrasound-offers-new-path-for-deep-brain-stimulation/
MIT researchers have developed a novel approach to deep brain stimulation using ultrasound, potentially offering a safer and longer-lasting alternative to traditional implanted electrodes. This hair-thin device, tested in mice, successfully triggered dopamine release in a brain region crucial for Parkinson’s disease treatment.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevTiny Flaws, Big Impact: Microscopic Defects Drive Glacier Flow, MIT Study Findshttps://thescience.dev/tiny-flaws-big-impact-microscopic-defects-drive-glacier-flow-mit-study-finds/
New research from MIT reveals that microscopic defects within ice play a crucial role in dictating the flow of massive glaciers, a finding with significant implications for predicting future sea-level rise.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevTurning Up the Heat on Next-Generation Semiconductorshttps://thescience.dev/turning-up-the-heat-on-next-generation-semiconductors/
MIT researchers explore the high-temperature performance of gallium nitride, paving the way for electronics that can withstand extreme environments like the surface of Venus.
2024-09-2905 min
The Science DevSeeing Clearly in Black and White: How Early Limitations Shape Visual Resiliencehttps://thescience.dev/seeing-clearly-in-black-and-white-how-early-limitations-shape-visual-resilience/
New research from MIT suggests that the brain’s ability to recognize objects in both color and black-and-white stems from the visual limitations experienced early in life. This early training in luminance-based object recognition may be key to developing a robust visual system.
2024-09-2912 min
The Science DevIlluminating Muscle Control: MIT Pioneers Light-Based Approach to Restoring Limb Functionhttps://thescience.dev/illuminating-muscle-control-mit-pioneers-light-based-approach-to-restoring-limb-function/
MIT researchers have developed a new approach that they hope could someday offer better muscle control with less fatigue. Instead of using electricity to stimulate muscles, they used light.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevA New Strategy to Cope With Emotional Stresshttps://thescience.dev/a-new-strategy-to-cope-with-emotional-stress/
A new study from MIT reveals a cognitive strategy focused on social good may be effective in helping people cope with distressing events, particularly those in emotionally demanding professions.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevResearchers Develop Scalable Hardware for Quantum Computershttps://thescience.dev/researchers-develop-scalable-hardware-for-quantum-computers/
MIT and MITRE researchers have unveiled a quantum-system-on-chip (QSoC) architecture, paving the way for large-scale quantum computers. This innovative approach integrates thousands of interconnected qubits onto a single chip, addressing a key challenge in quantum computing development.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevNew Wireless Receiver Combats Interference for Superior Mobile Performancehttps://thescience.dev/new-wireless-receiver-combats-interference-for-superior-mobile-performance/
MIT researchers have developed a novel wireless receiver architecture that effectively combatsinterference, improving performance in 5G and future 6G devices. This innovation addresses the growing challenge of crowded airwaves as wireless communication demands increase.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevMapping the Mind: New Technologies Allow 3D Imaging of Whole Human Brain Hemispheres at Subcellular Resolutionhttps://thescience.dev/mapping-the-mind-new-technologies-allow-3d-imaging-of-whole-human-brain-hemispheres-at-subcellular-resolution/
A groundbreaking new study published in Science details a technological pipeline that allows researchers to process, label, and image entire hemispheres of human brains at unprecedented resolution and speed. This advancement opens doors to a deeper understanding of the human brain in both health and disease.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevJurassic Park Meets Reality: Scientists Preserve DNA in Amber-Like Polymerhttps://thescience.dev/jurassic-park-meets-reality-scientists-preserve-dna-in-amber-like-polymer/
Inspired by the movie Jurassic Park, MIT researchers have developed a revolutionary method for storing DNA at room temperature using a glassy, amber-like polymer. This breakthrough could transform how we preserve genetic information and digital data for generations to come.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevA Technique for More Effective Multipurpose Robotshttps://thescience.dev/a-technique-for-more-effective-multipurpose-robots/
MIT researchers developed a technique to combine multiple sources of data across domains, modalities, and tasks using a type of generative AI known as diffusion models. This approach enabled a robot to perform multiple tool-use tasks and adapt to new tasks it did not see during training.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevWater-Soluble Enzyme Opens Doors for New Antibiotic Developmenthttps://thescience.dev/water-soluble-enzyme-opens-doors-for-new-antibiotic-development/
MIT researchers have developed a method to make a key bacterial enzyme water-soluble, potentially paving the way for a new class of antibiotics to combat antibiotic resistance.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevThe exponential growth of AI computationhttps://thescience.dev/the-exponential-growth-of-ai-computation/
The exponential increase in the development and computation of AI models will be a major energy concern in the coming days.
2024-09-2905 min
The Science DevSwirling electrons detected in graphenehttps://thescience.dev/swirling-electrons-detected-in-graphene/
Using a highly sensitive quantum sensor, researchers have directly observed electron vortices forming in micrometer-sized graphene disks, shedding light on the unique fluid-like behavior of electrons in this wonder material.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevThe Cotton Candy Planet: Astronomers Discover a Giant, Super-Light Worldhttps://thescience.dev/the-cotton-candy-planet-astronomers-discover-a-giant-super-light-world/
A newly discovered planet, WASP-193b, is as large as Jupiter but with a density comparable to cotton candy, baffling scientists with its unusual formation.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevAncient Stars Discovered in the Milky Way’s Halohttps://thescience.dev/ancient-stars-discovered-in-the-milky-ways-halo/
MIT researchers have discovered three of the oldest stars in the universe, right in our own galactic backyard, providing a glimpse into the early universe.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevAffordable Lead Detection: A New Chip Offers Hope for Clean Waterhttps://thescience.dev/affordable-lead-detection-a-new-chip-offers-hope-for-clean-water/
A new, inexpensive chip can detect lead in water at incredibly low concentrations, potentially revolutionizing how we monitor and combat lead contamination.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevHow AI Is Unlocking the Secrets of Matterhttps://thescience.dev/how-ai-is-unlocking-the-secrets-of-matter/
Scientists from MIT and the University of Basel are harnessing the power of generative AI to automatically map out phase diagrams, paving the way for the discovery of unknown phases of matter.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevRepurposed Yeast Tackles Lead Contamination in Waterhttps://thescience.dev/repurposed-yeast-tackles-lead-contamination-in-water/
Discarded brewery yeast could hold the key to removing lead from contaminated water, offering a cost-effective and sustainable solution to a persistent environmental challenge.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevIlluminating the Brain: A New Technique for Deep-Brain Imaginghttps://thescience.dev/illuminating-the-brain-a-new-technique-for-deep-brain-imaging/
MIT engineers have developed a groundbreaking technique called BLUSH that uses MRI to detect light deep within the brain, opening new avenues for understanding brain function.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevMIT Researchers Develop a Revolutionary, Reusable Toxic Gas Detectorhttps://thescience.dev/mit-researchers-develop-a-revolutionary-reusable-toxic-gas-detector/
MIT researchers have combined metal-organic frameworks with polymers to create a low-cost, reusable, and highly sensitive gas detector that could revolutionize toxic gas monitoring in homes and industrial settings.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevAncient Quasars Reveal Clues about Early Black Hole Growthhttps://thescience.dev/ancient-quasars-reveal-clues-about-early-black-hole-growth/
These black holes are billions of times more massive than the sun, at a time when the universe is still in its infancy.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevBeyond the Wavelength: Scientists Achieve Unprecedented Atomic Proximityhttps://thescience.dev/beyond-the-wavelength-scientists-achieve-unprecedented-atomic-proximity/
MIT physicists have developed a technique to arrange atoms at distances as small as 50 nanometers, a tenfold improvement over conventional methods, opening doors to a new regime of quantum phenomena.
2024-09-2906 min
The Science DevTen years of neuroscience at Google yields maps of human brainhttps://thescience.dev/ten-years-of-neuroscience-at-google-yields-maps-of-human-brain/
A piece of human brain tissue the size of half a grain of rice requires 1.4 petabytes of storage.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevPredicting the unpredictable: New algorithm improves extreme weather forecastshttps://thescience.dev/predicting-the-unpredictable-new-algorithm-improves-extreme-weather-forecasts/
MIT researchers develop a method to refine climate models and predict the frequency of extreme weather events with greater accuracy.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevPeering into the heart of darkness: AI reconstructs 3D video of black hole flarehttps://thescience.dev/peering-into-the-heart-of-darkness-ai-reconstructs-3d-video-of-black-hole-flare/
Scientists use AI and telescope data to create the first 3D reconstruction of a flares of black hole.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevTuning the entanglement structure in an array of qubitshttps://thescience.dev/tuning-the-entanglement-structure-in-an-array-of-qubits/
MIT researchers have developed a groundbreaking technique to manipulate entanglement in superconducting qubits, offering valuable insights into the fundamental resource of quantum computing.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevEarths magnetic shield older and stronger than we thoughthttps://thescience.dev/earths-magnetic-shield-older-and-stronger-than-we-thought/
New evidence suggests Earth’s magnetic field existed earlier than previously believed, potentially playing a crucial role in the emergence of life.
2024-09-2910 min
The Science DevHow light can vaporize water without the need for heathttps://thescience.dev/how-light-can-vaporize-water-without-the-need-for-heat/
MIT scientists uncover a surprising phenomenon where light directly triggers water evaporation, with potential implications for climate modeling and desalination technology.
2024-09-2909 min
The Science DevUnveiling-the-secrets-of-star-formation-a-new-molecule-emerges-in-spacehttps://thescience.dev/unveiling-the-secrets-of-star-formation-a-new-molecule-emerges-in-space/
A team of researchers, led by MIT Professor Brett McGuire, has made a groundbreaking discovery – the detection of a previously unknown molecule within the vast expanse of space.
2024-09-2908 min
The Science DevAI-designs-new-drugs-based-on-protein-structureshttps://thescience.dev/ai-designs-new-drugs-based-on-protein-structures/
A new AI model developed by chemists at ETH Zurich makes it possible to generate active pharmaceutical ingredients quickly and easily based on a protein’s three-dimensional surface. The new process could revolutionize drug research.
2024-09-2907 min
The Science DevTen years of neuroscience at Google yields maps of human brainhttps://thescience.dev/ten-years-of-neuroscience-at-google-yields-maps-of-human-brain/
Google researchers, in collaboration with Harvard University, have reconstructed a tiny piece of the human brain at an unprecedented level of detail, revealing never-before-seen structures and paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in neuroscience.
2024-05-1003 min
The Science DevAn ink for 3D-printing flexible devices without mechanical jointsEPFL researchers target the next generation of soft actuators and robots with elastomer-based ink for 3D printing objects with locally changing mechanical properties, eliminating the need for cumbersome mechanical joints.
https://thescience.dev/an-ink-for-3d-printing-flexible-devices-without-mechanical-joints/
2024-04-2303 min
The Science DevEnergy scientists unravel the mystery of gold’s glowLuminescence, or the emission of photons by a substance exposed to light, has been known to occur in semiconductor materials like silicon for hundreds of years.
https://thescience.dev/energy-scientists-unravel-the-mystery-of-golds-glow/
2024-04-2304 min
The Science DevTropical forests can’t recover naturally without fruit eating birdsNew research from the Crowther Lab at ETH Zurich illustrates a critical barrier to the natural regeneration of tropical forests.
https://thescience.dev/tropical-forests-cant-recover-naturally-without-fruit-eating-birds/
2024-04-2305 min
The Science DevSurprising reversal in quantum systemsQuantum systems in physics can also have a specific apple or doughnut topology, which manifests itself in the energy states and motion of particles.
https://thescience.dev/surprising-reversal-in-quantum-systems/
2024-04-2004 min
The Science DevJupiter’s moon Io has been volcanically active for billions of yearsIo, Europa, and Ganymede are in an orbital configuration known as a Laplace resonance: For every orbit of Ganymede , Europa completes exactly two orbits, and Io completes exactly four.
https://thescience.dev/jupiters-moon-io-has-been-volcanically-active-for-billions-of-years/
2024-04-2004 min
The Science DevA new type of seismic sensor to detect moonquakesUnlike the Earth, the Moon is not tectonically active. Lunar quakes have different origins: Some are caused by day-to-night thermal differences as the surface varies in temperature.
https://thescience.dev/a-new-type-of-seismic-sensor-to-detect-moonquakes/
2024-04-2003 min
The Science DevQuantum sensors to image Meissner effect in hydride supercondutorshttps://thescience.dev/quantum-sensors-to-image-meissner-effect-in-hydride-supercondutors/
Hydrogen (like many of us) acts weird under pressure. Theory predicts that when crushed by the weight of more than a million times the Earth’s atmosphere, this light, abundant, normally gaseous element first becomes a metal, and even more strangely, a superconductor – a material that conducts electricity with no resistance.
2024-04-2003 min
The Science DevQuantum crystal of frozen electrons visualizedScientists at Princeton University have made a groundbreaking discovery by visualizing a Wigner crystal for the first time.
https://thescience.dev/quantum-crystal-of-frozen-electrons-visualized/
2024-04-2002 min
The Science DevCraving snacks after a meal? It might be food-seeking neurons, not an overactive appetiteIndividuals who often find themselves searching for snacks shortly after a substantial meal may be experiencing the effects of hyperactive neurons responsible for food-seeking behavior rather than an increased appetite.
https://thescience.dev/craving-snacks-after-a-meal-it-might-be-food-seeking-neurons-not-an-overactive-appetite/
2024-04-2003 min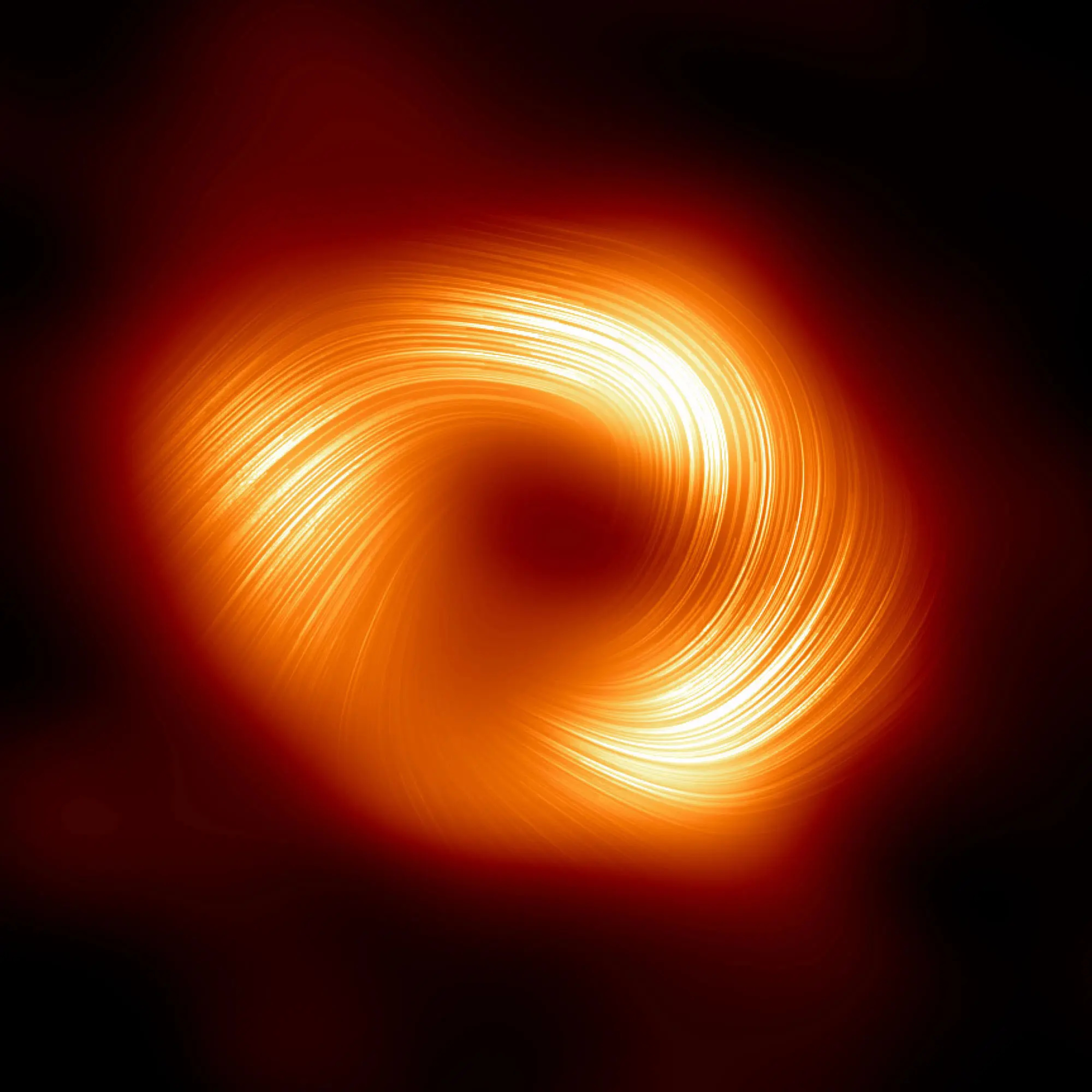
The Science DevStrong magnetic fields spiraling at the edge of the Milky Way’s central black holeThe recent study presents an unprecedented glimpse into the complex dynamics surrounding the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A star at the center of our Milky Way Galaxy.
https://thescience.dev/strong-magnetic-fields-spiraling-at-the-edge-of-the-milky-ways-central-black-hole/
2024-04-2003 min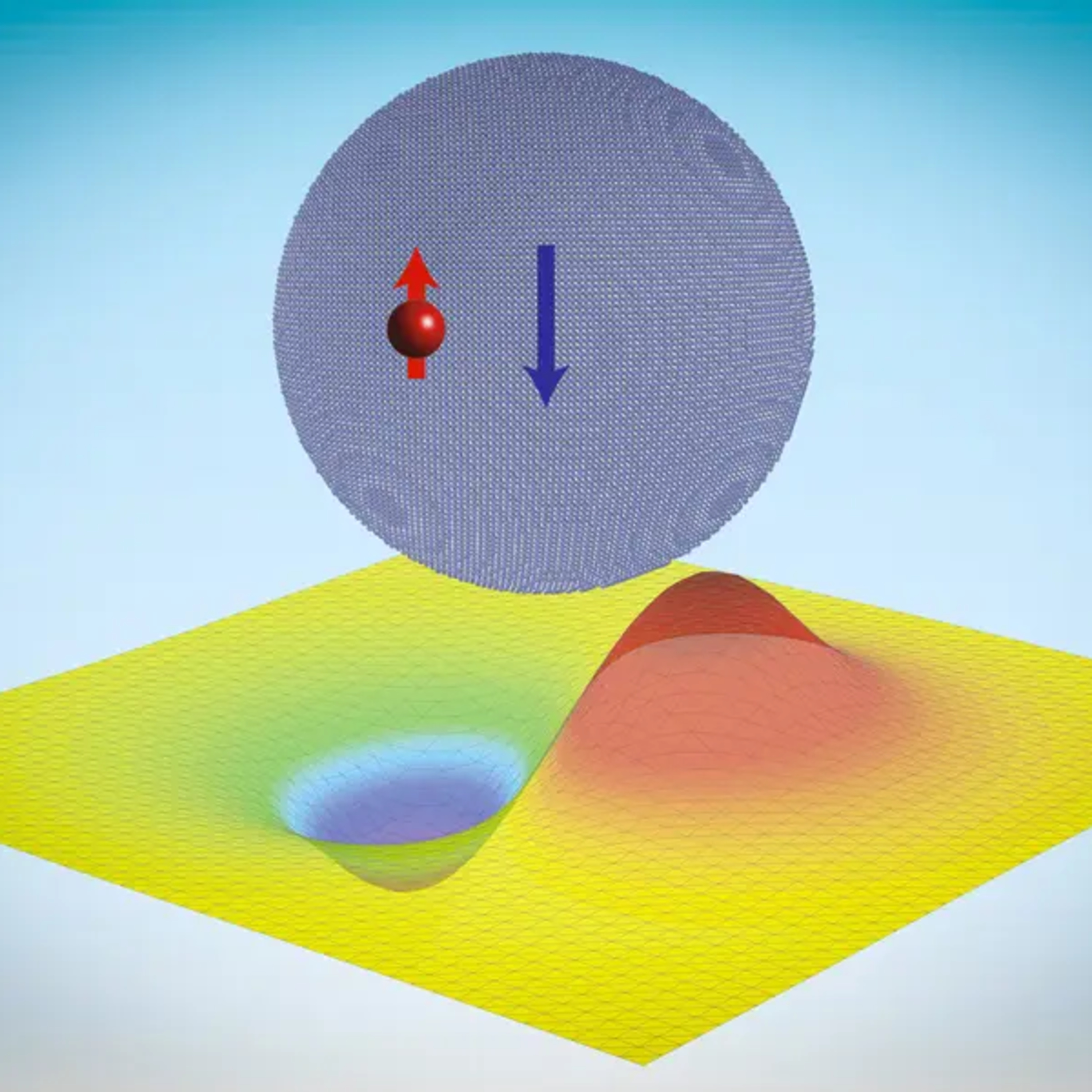
The Science DevNeutrons can bind to quantum dotsNeutrons can bind to quantum dots solely through the strong force, which typically only operates at the atomic nucleus level.
https://thescience.dev/neutrons-can-bind-to-quantum-dots/
2024-04-2002 min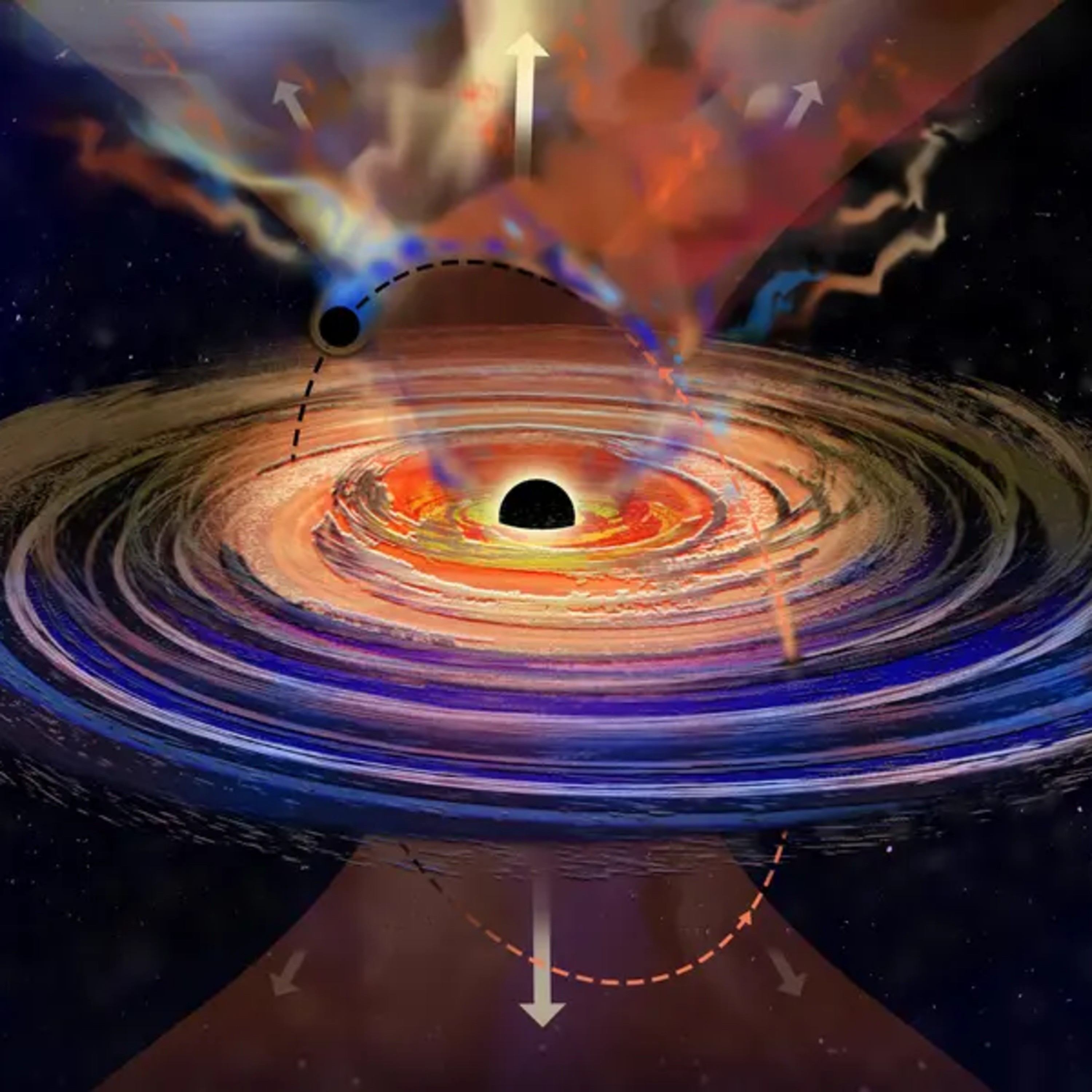
The Science DevHiccups in a black hole are likely due to another punching black holeIn a distant galaxy, astronomers have detected unusual activity from a supermassive black hole, previously known for its silence.
https://thescience.dev/hiccups-in-a-black-hole-are-likely-due-to-another-punching-black-hole/
2024-04-2002 min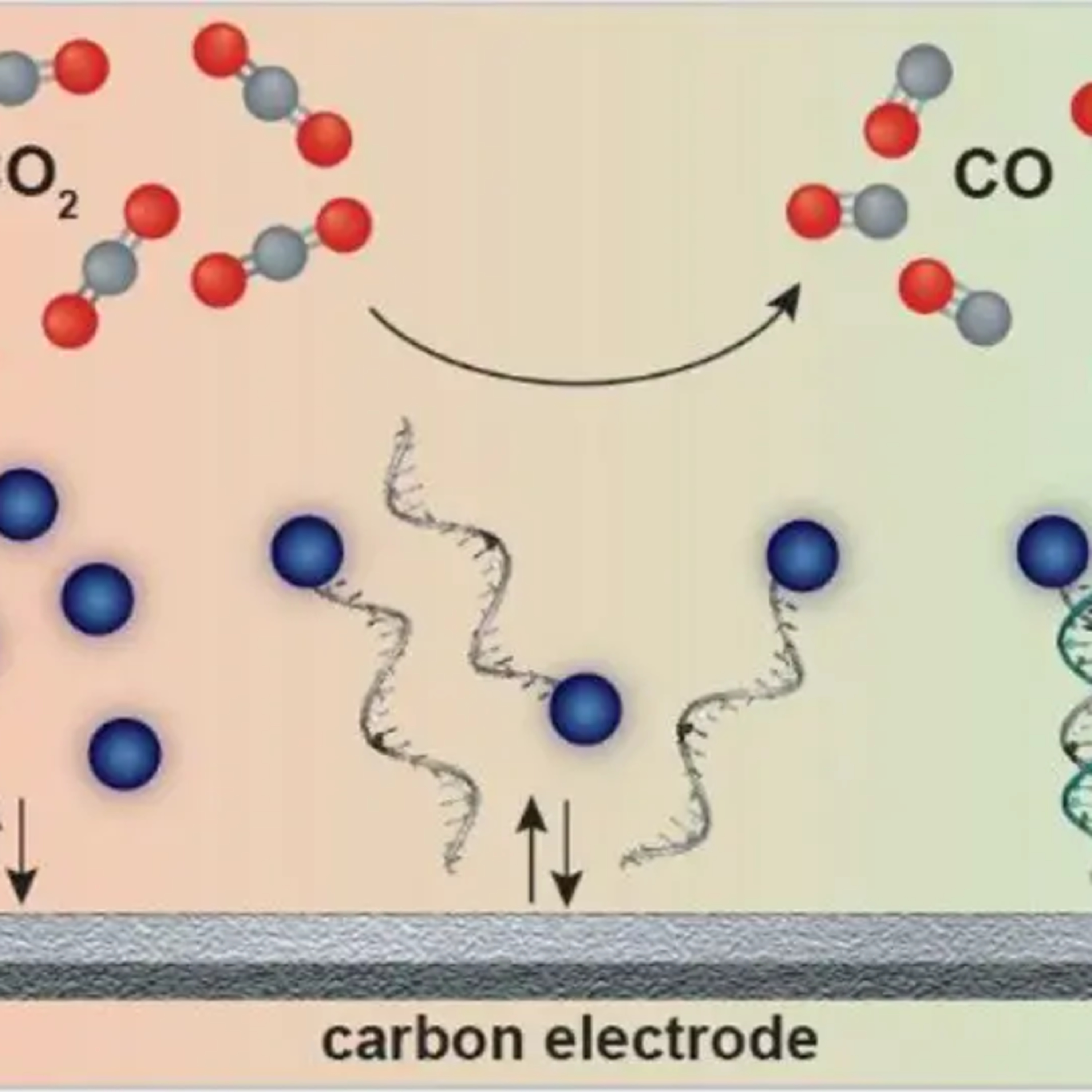
The Science DevCatalysts tethered by DNA convert carbon dioxide into useful productshttps://thescience.dev/catalysts-tethered-by-dna-convert-carbon-dioxide-into-useful-products/
MIT chemical engineers have pioneered a method to transform carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide, a key intermediary for synthesizing valuable chemicals like ethanol and other fuels.
2024-04-2002 min
The Science DevPropelling atomically layered magnets toward green computersA notable shift in research has been towards the exploration of two-dimensional van der Waals magnets, a new class of magnetic materials that hold the promise of superior scalability and energy efficiency.
https://thescience.dev/propelling-atomically-layered-magnets-toward-green-computers/
2024-04-2004 min
The Science DevMolecular weaving makes polymer composites strongerAt its most basic, chemistry is a lot like working with building blocks – but the materials are atoms and molecules.
https://thescience.dev/molecular-weaving-makes-polymer-composites-stronger/
2024-04-1904 min
The Science DevBetter radiation detectors with the inspiration from TetrisThe device, based on simple tetromino shapes, could determine the direction and distance of a radiation source, with fewer detector pixels.
https://thescience.dev/better-radiation-detectors-with-the-inspiration-from-tetris/
2024-04-1906 min
The Science DevHow Microsoft and Quantinuum achieved reliable quantum computingBy applying an innovative qubit-virtualization system to ion-trap hardware, Microsoft and Quantinuum were able to create four highly reliable logical qubits from only 30 physical qubits, while demonstrating an 800x improvement in error rate.
https://thescience.dev/how-microsoft-and-quantinuum-achieved-reliable-quantum-computing/
2024-04-1903 min
The Science DevTeaching Nature to Break Man-made Chemical BondsFor the first time, scientists have engineered an enzyme that can break stubborn man-made bonds between silicon and carbon that exist in widely used chemicals known as siloxanes, or silicones. The discovery is a first step toward rendering the chemicals, which can linger in the environment, biodegradable.
https://thescience.dev/teaching-nature-to-break-man-made-chemical-bonds/
2024-04-1901 min
Tollywood KaburluRevisiting Mr. Perfect (2011): Review + Interesting FactsCredits
Banner: Sri Venkateswara Creations
Cast: Prabhas, Kajal Agarwal, Tapsee, Prakash Raj, K Viswanath, Murali Mohan, Nassar, Sayaji Shinde, Brahmanandam, Raghubabu, Master Bharat, Sameer, Kasi Viswanath, Raja Ravindra, Kaushal Prasad, Krishnudu, Subbaraya Sharma, Pragati, Tulasi, Rajitha, Sagar, Satyadev Kancharana
Music: Devi Sri Prasad
Cinematography: Vijay K Chakravarthy
Art: Ravinder
Editor: Marthand K Venkatesh
Fights: Peter Heins
Screenplay: Hari
Dialogues: Abburi Ravi
Story - Direction: K Dasaradh
Producer: Dil Raju
Release date: 22 April 2011
Interesting Facts Links:
https://www.idlebrain.com/celeb/interview...
2023-03-2144 min