Shows
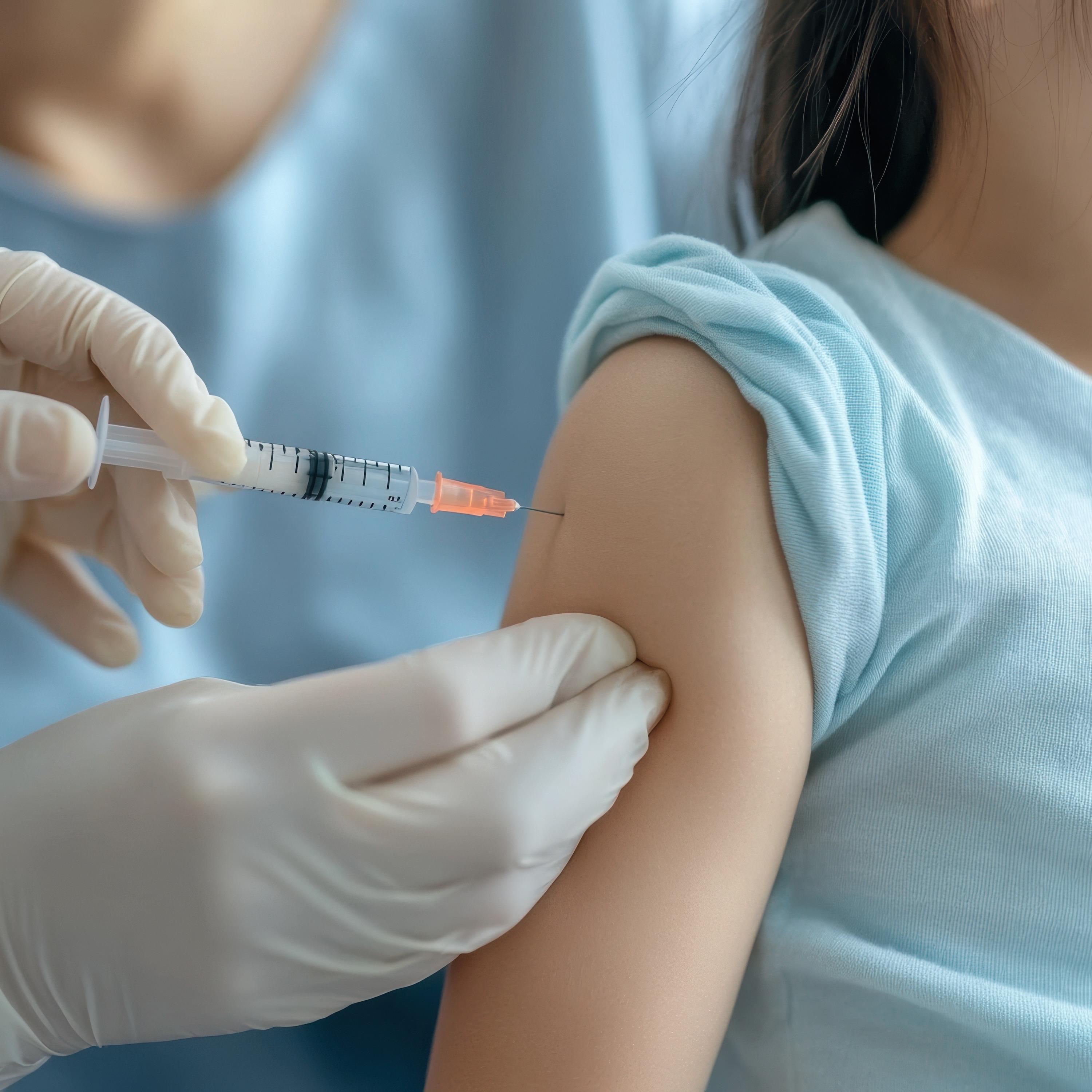
EMplify by EB MedicineMeasles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella with Dr Tim HoreczkoIn this episode, Sam Ashoo, MD and Tim Horeczko, MD discuss the November 2025 Pediatric Emergency Medicine Practice article, Emergency Department Management of Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella in Pediatric Patients00:00 Introduction to Emergency Medicine00:21 Welcome and Holiday Greetings01:16 Special Guest Introduction01:41 Discussion on Pediatric Emergency Medicine04:55 Epidemiology of Measles08:16 Challenges in Diagnosing Measles14:27 Mumps: Symptoms and Complications27:36 Rubella: Risks and Symptoms29:28 Varicella: Symptoms and Precautions33:12 Differential Diagnosis and Conclusion35:14 Using Inductive Reasoning in Medical Di...
2025-12-1134 min 2024-03-0125 min
2024-03-0125 min 2023-12-0116 min
2023-12-0116 min 2023-09-0108 min
2023-09-0108 min 2023-08-0134 min
2023-08-0134 min 2023-07-0131 min
2023-07-0131 min 2023-06-0138 min
2023-06-0138 min 2023-05-0117 min
2023-05-0117 min 2023-04-0148 min
2023-04-0148 min 2023-03-0127 min
2023-03-0127 min 2023-02-0131 min
2023-02-0131 min 2023-01-0127 min
2023-01-0127 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookEnvironmental Injuries in Children pemplaybook.org/podcast/environmental-injuries-in-children/
2022-12-0139 min 2022-11-0138 min
2022-11-0138 min 2022-10-0128 min
2022-10-0128 min 2022-09-0148 min
2022-09-0148 min 2022-08-0144 min
2022-08-0144 min 2022-07-0119 min
2022-07-0119 min 2022-06-0130 min
2022-06-0130 min 2022-05-0123 min
2022-05-0123 min 2022-04-0125 min
2022-04-0125 min 2022-03-0130 min
2022-03-0130 min 2022-02-0127 min
2022-02-0127 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookFocus On: Pyloric Stenosis Myth: “No olive, no problem” Reality: Rare finding, since we diagnose earlier Pyloric stenosis occurs in young infants because the pyloric sphincter hypertrophies, causing near-complete obstruction of the gastric outlet. More common in boys, preterm babies, first-born. Less common in older mothers. Association with macrolide use. Presentation Young infant arrives with forceful vomiting, but can’t quite get enough to eat “the hungry, hungry, not-so-hippo”. Early presentation from 3 to 5 weeks of age: projectile vomiting Later presentation up to 12 weeks: dehydration, failure to thrive, possibly t...
2022-01-0116 min 2021-12-0131 min
2021-12-0131 min 2021-11-0117 min
2021-11-0117 min 2021-10-0134 min
2021-10-0134 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookFocus On: Inguinal Hernias in ChildrenHernia Myth: “If it’s not strangulated, it’s elective” Reality: Unlike in adults, all hernias in children are repaired at the time of diagnosis because: The risk of incarceration and strangulation is high There is a 30% risk of testicular infarction due to pressure on the gonadal vessels It is not worth messing around and “trying to navigate the system” Most groin hernias in children are indirect inguinal hernias (incomplete closure of processus vaginalis). Most indirect hernias are in boys (10-fold risk), and on the right (60%). Premature babies are at higher risk as well...
2021-09-0113 min 2021-08-0120 min
2021-08-0120 min 2021-07-0114 min
2021-07-0114 min 2021-06-0132 min
2021-06-0132 min 2021-05-0142 min
2021-05-0142 min 2021-04-0137 min
2021-04-0137 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookConstipation and the way outConstipation as a diagnosis can be dangerous, mainly because it is a powerful anchor in our medical decision-making. Chances are, you’d be right to chalk up the pain to functional constipation — 90% of pediatric constipation is functional, multifactorial, and mostly benign — as long as it is addressed. We’re not here for “chances are“; we’re here for “why isn’t it?“ Ask yourself, could it be: Anatomic malformations: anal stenosis, anterior displaced anus, sacral hematoma Metabolic: hypothyroidism, hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, cystic fibrosis, diabetes mellitus, gluten enteropathy Neuropathic: spinal cord abnormalitie...
2021-03-0148 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPediatric IV Tips and TricksTop 10 [details in audio] Set the stage – exude confidence and be prepared Choose the right cannula size – a smaller working IV is infinitely better than none Feeling is better than looking – trust yourself Mark the site – things get wonky when you take your hands off to disinfect Tourniquets can mess you up – try to use a holder’s hand to occlude the vein The holder rules – get as many hands on deck as you need. Tension is good – a little counter traction on the skin with you...
2021-02-0126 min 2021-01-0128 min
2021-01-0128 min 2020-12-0144 min
2020-12-0144 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookGo or No Go: Pediatric Presedation Assessmenthttps://pemplaybook.org/?p=2211
2020-11-0143 min 2020-10-0132 min
2020-10-0132 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPediatric Hand FracturesTuft Fracture Yeh PC et al. Pediatric Hand Fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2009. Seymour Fracture Nellans et al. Pediatric Hand Injuires. Hand Clin. 2013 November ; 29(4): 569–578 Yeh PC et al. Pediatric Hand Fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2009. Mallet Fracture Adolescent with mallet finger and Kirschner wire fixation. Nellans et al. Pediatric Hand Injuires. Hand Clin. 2013 November ; 29(4): 569–578 Mallet finger in splint. Yeh PC et al. Pediatric Hand Fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2009. Volar Plate Injury Yeh PC et al. Pediatric Hand Fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2009. Central Slip Injury Lee SA et al. Ultrasonography of t...
2020-09-0143 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookHeat-Related IllnessA spectrum — but will you recognize the blurry signposts? Temperature (core) Presentation Management Miliaria Crystallina Normal Salt-colored tiny papules, easily burst; not pruritic Modify environment; light clothing; hydration Miliaria Rubra Normal Discrimiate, red papules, not assocaited with follicles; pruritic Above plus cool compresses; calamine lotion; symptomatic tx for pruritis Miliaria Profunda Normal Confluent flesh-colored, “lumpy-bumpy”; burning Same as rubra Miliaria Pustulosa Normal May resemble rubra and/or crustallina, but pustular; h/o previous dermatitis Same as above, but may may need antibiotic if no improvement over time Heat edema Normal Swelling of feet, ankles, and/or lower legs Modify environment; elev...
2020-08-0144 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookDiarrhea Traditional Approach: Secretory -- poisoned mucosal villi -- "the sieve" Cytotoxic -- destroyed mucosal villi -- "the shred" Osmotic -- malabsorption -- "the pull" Inflammatory -- edema, motility -- "the push" Lots of overlap, difficult to apply to clinical signs and symptoms. Bedside Approach: Fever/No Fever, Bloody/No Blood Non-bloody, febrile -- most likely viral Non-bloody, afebrile -- may be viral Bloody, febrile -- likely bacterial Non-bloody, afebrile -- full stop. Eval f...
2020-07-0150 min 2020-06-0145 min
2020-06-0145 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookZen and the Art of Pediatric Readiness Pediatric Readiness is not just an ideal -- it's a tangible plan, a toolkit, and even better, an attitude How to improve your institution, and your own personal pediatric readiness. National Pediatric Readiness Project (NPRP) Los Angeles County Pediatric Readiness Project
2020-05-0130 min 2020-04-0144 min
2020-04-0144 min 2020-03-0150 min
2020-03-0150 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookMajor Burns in Children Lund and Browder Chart to Estimate Burn Size in Children
2020-02-0143 min 2020-01-0143 min
2020-01-0143 min 2019-12-0139 min
2019-12-0139 min 2019-11-0145 min
2019-11-0145 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookNeck Masses in ChildrenThe differential diagnosis is long... You need an approach. The Rule of 3s: 3 minutes -- Traumatic 3 days -- Inflammatory 3 months -- Neoplastic 3 years -- Congenital 3 Minutes? Traumatic 3 Days? Inflammatory [caption id="attachment_1777" align="alignnone" width="262"] Cervical Node Chain; Lymphadenopathy[/caption] [caption id="attachment_1773" align="alignnone" width="298"] Bacterial Lymphadenitis[/caption] [caption id="attachment_1772" align="alignnone" width="300"] Bacterial lymphadenitis with small abscess[/caption] [caption id="attachment_1771" align="alignnone" width="300"] Large Abscess[/caption] 3 M...
2019-10-0139 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookIntraosseous Devices https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cQVKIpLc8bk Selected References Barnard, et al. Rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia via the intraosseous route: a prospective observational study. Emerg Med J. 2014; Jun 24. pii: emermed-2014-203740. Jousi M, Saikko S, Nurmi J. Intraosseous blood samples for point-of-care analysis: agreement between intraosseous and arterial analyses. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2017;25(1):92. Published 2017 Sep 11. doi:10.1186/s13049-017-0435-4 Knuth, et al. Intraosseous Injection of Iodinated Computed Tomography Contrast Agent in an Adult Blunt Trauma Patient. Annals o...
2019-09-0146 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookCyanosis Your eyes may fool you... Keep your differential diagnosis open. Selected References Aravindhan N, Chisholm DG. Sulfhemoglobinemia presenting as pulse oximetry desaturations. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:883–884. Gharahbaghian L et al. Methemoglobinemia and Sulfhemoglobinemia in Two Pediatric Patients after Ingestion of Hydroxylamine Sulfate. West J Emerg Med. 2009 Aug; 10(3): 197–201
2019-08-0136 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookFailure to Thrive Failure to Thrive (FTT) is not just for the clinics. We need to be on the lookout, because if we find it, there is already a big problem. Definitions of Failure to Thrive may quibble on the details, but for us in the ED: Consistently under 2nd percentile in weight over time "Falling off" the growth curve over 2 or more points We can get around the longitudinal requirement by looking at weight as a "spot check" -- if grossly below weight without any other chronic condition, be...
2019-07-0136 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookMass Casualty Incident No one ever wants to find himself in this situation. A factory explodes. A building catches fire. A multi-vehicle traffic collision. Or an act of terrorism. Very quickly, we have to scrap business as usual. We have to adapt to our new circumstances. Definition of a mass casualty incident (MCI): An incident which produces multiple casualties such that emergency services, medical personnel and referral systems within the normal catchment area cannot provide adequate and timely response and care without unacceptable mortality and/or morbidity. In other words, our demand far outpaces our reso...
2019-06-0132 min 2019-05-0136 min
2019-05-0136 min 2019-04-0134 min
2019-04-0134 min 2019-03-0143 min
2019-03-0143 min 2019-02-0126 min
2019-02-0126 min 2019-01-0112 min
2019-01-0112 min 2018-12-0114 min
2018-12-0114 min 2018-11-0121 min
2018-11-0121 min 2018-10-0133 min
2018-10-0133 min 2018-09-0134 min
2018-09-0134 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookStrep ThroatDoes Your Patient Have Streptococcal Pharyngitis? No Problem -- I'll just Swab. Not So Fast... Fagan Nomogram for Likelihood Ratios 1. Decide on your pre-test probability of the disease (choose an approximate probability based on our assessment) 2. Use the likelihood ratio that correlates to your exam. 3. Draw a straight line frm your pre-test probability starting point, to the LR of the feauture/test, take it through to find your post-test probability 4. Use this new post-test probability to help in your decision Your patient has palatal petechiae, which confers a positive likelihood ratio (LR+) of 2.7 S...
2018-08-0141 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookConcussionHow do we make the diagnosis? What now? Concussion in Sport Group Guidelines Concussion Recognition Tool (for coaches, trainers on field) Child Sports Concussion Assessment Tool, 5th Ed. (Child SCAT); Ages 5-12 Sports Concussion Assessment Tool, 5th Ed. (SCAT5); Ages 13 and Up This post and podcast are dedicated to the great K Kay Moody, DO, MPH for her stalwart effort to care for both patient and doctor. Thank you for all that you do to help us to be our best and for promoting #FOAMed #F...
2018-07-0134 min 2018-06-0120 min
2018-06-0120 min 2018-05-0137 min
2018-05-0137 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookHypertension in Children References Baracco R et al. Pediatric Hypertensive Emergencies. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014; 16:456. Belsha CW. Pediatric Hypertension in the Emergency Department. Ann Emerg Med. 2008; 51(3):21-24. Chandar J et al. Hypertensive crisis in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:741-751. Dionne JM et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2017 Guidelines for the Diagnosis, Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment of Pediatric Hypertension. Canadian J Cardiol. 2017; 33:577-585 *Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al; SUBCOMMITTEE ON SCREENING AND MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN CHILDREN. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Chi...
2018-04-0130 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookThe Fussy InfantA Social Visit or Your Most Dangerous Presentation Tonight? [Details in Audio] This post and podcast are dedicated to Henry Goldstein, B.Pharm, MBBS for his tireless dedication to all things #FOAMed, #FOAMped, and #MedEd. You are awesome. Make sure to visit
2018-03-0146 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookAirway Master MovesYou know how to intubate safely. You can recite all of the Ps backwards and forwards. Until you can't. Real-time trouble-shooting. [Details in Audio] This post and podcast are dedicated to Mads Astvad for sharing his enthusiasm, clinical excellence, and #FOAMed warrior spirit. Tak, min ven! #SMACConia #Vikingeblod
2018-02-0120 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookOvarian TorsionOvarian torsion is like the MI of the pelvis. Sometimes all it takes is a good story to investigate. When to worry, when to walk it off, and when to work it up: What is the typical presentation of ovarian torsion? There is none. The presentation varies so much, we need a rule to live by: Unilateral pelvic pain in a girl is ovarian torsion until proven otherwise. This includes the cases in which you are concerned about appendicitis. They both can be fake-outs. Often the pain is severe and abrupt, but tr...
2018-01-0124 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookJust Say No To (These) DrugsDogma often dictates routine care. There are times when we have to attend to paradigm shifts. An easy way to save lives? Just say no to (these) drugs: Codeine Normally metabolized into codeine-6-glucuronide (50-70%) and norcodeine (10-15%). Codeine, codeine-6-glucuronide, and norcodeine have low affinity for the μ (mu) receptor. However, the most active metabolite of codeine is morphine with 200x the affinity for the mu receptor as the codeine derivates. The problem is, people vary in its metabolism from 0-15% of codeine is metabolized to morphine. Ok, codeine is lame at best, unpredictable at worst...
2017-12-0125 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookBlunt Head TraumaNot all head trauma is minor. Not all minor head trauma is clinically significant. How can we sort out the overtly ok from the sneakily serious? Mnemonics for bedside risk stratification of minor pediatric blunt head trauma, based on PECARN studies: [Details in Audio] Blunt Head Trauma in Children < > Blunt Head Trauma in Children ≥ 2 years of Age Image Gently Campaign Medical Imaging Record (main...
2017-11-0130 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookThe Higher Tech Kid in the EDComfortable with G-tubes, tracheostomies, and VP shunts? Good. Get ready for the next level: Vagus Nerve Stimulators, Intrathecal Pumps, and Ventricular Assist Devices. Details in Audio: Vagus Nerve Stimulators For intractable epilepsy; sends retrograde signal up corona radiata Also may be used in: depression, bulimia, Alzheimer, narcolepsy, addiction, and others VNS magnets Are VNS safe in MRI? Are VNS safe in everyday life? Intrathecal Pumps Used to infuse basal rate of drug, usually baclofen for spasticity, but pump may contain morphine, bupivicaine, clonidine. Also used for...
2017-10-0131 min 2017-09-0135 min
2017-09-0135 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookThe Pediatric Surgical AbdomenAbdominal pain is common; so are strongly held myths and legends about what is concerning, and what is not. One of our largest responsibilities in the Emergency Department is sorting out benign from surgical or medical causes of abdominal pain. Morbidity and mortality varies by age and condition. Abdominal Surgical Emergencies in Children: A Relative Timeline General Advice Neonate (birth to one month) Necrotizing Enterocolitis Pneumatosis Intestinalis. Essentials: Typically presents in 1st week of life (case reports to 6 months in chronically ill children) Extend suspicion longer in NICU graduates Up to...
2017-08-0130 min 2017-07-0139 min
2017-07-0139 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookMI in ChildrenMyocardial infarction (MI) in children is uncommon, but underdiagnosed. This is due to two main factors: the etiologies are varied; and the presenting symptoms are “atypical”. We need a mental metal detector! Case examples Congenital Two main presentations of MI due to congenital lesions: novel and known. The novel presentation is at risk for underdiagnosis, due to its uncommonness and vague, atypical symptoms. There are usually some red flags with a careful H&P. The known presentation is a child with a history of congenital heart disease, addressed by corrective or palliative surgery. This child is at risk...
2017-06-0136 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookNeonatal JaundiceMost newborns will have some jaundice. Most jaundice is benign. So, how can we sort through the various presentations and keep our newborns safe? Pathologic Jaundice When a baby is born with jaundice, it’s always bad. This is pathologic jaundice, and it’s almost always caught before the baby goes home. Think about ABO-incompatbility, G6PD deficiency, Crigler-Najjar, metabolic disturbances, and infections to name a few. Newborns are typically screened and managed. Physiologic Jaundice Physiologic jaundice, on the other hand, is usually fine, until it’s not. All babies have some inclination to develop jaundice. ...
2017-05-0139 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookForeign Bodies in the Head and NeckChildren the world over are fascinated with what can possibly “fit” in their orifices. Diagnosis is often delayed. Anxiety abounds before and during evaluation and management. Most common objects:1,2 Food Coins Toys Insects Balls, marbles Balloons Magnets Crayon Hair accessories, bows Beads Pebbles Erasers Pen/marker caps Button batteries Plastic bags, packaging Non-pharmacologic techniques Set the scene and control the environment. Limit the number of people in the room, the noise level, and minimize “cross-talk”. The focus should be on engaging, calming, and distracting the child. Quiet room; calm parent; “burrito wrap”; guided imagery; have a willing parent restrain th...
2017-04-0146 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookSupraglottic AirwaysWhen you give only after you're asked, you've waited too long. – John Mason First, learn to bag Place a towel roll under the scapulae to align oral, pharyngeal, and tracheal axes: Karsli C. Can J Anesth. 2015. Use airway adjuncts such as the oropharyngeal airway or a nasal trumpet. Use the two-hand ventilation technique whenever possible: (See Adventures in RSI for more) Supraglottic Airways: for difficult bag-valve-mask ventilation or a difficult airway (details in audio) LMA Classic Pros: Best studied; sizes for all a...
2017-03-0132 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookUrine TroubleWhen should you commit to getting urine? When can you wait? When should you forgo testing altogether? When do I get urine? Symptoms – either typical dysuria, urgency, frequency in a verbal child, or non-descript abdominal pain or vomiting in a well appearing child. Fever – but first look for an obvious alternative source, especially viral signs or symptoms. No obvious source? Risk stratify before “just getting a urine”. In a low risk child, with obviously very vigilant parents, who is well appearing, you may choose not to test now, and ensure c...
2017-02-0152 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPediatric PainN.B.: This month's show notes are a departure from the usual summary. Below is a reprint (with permission) of a soon-to-be released chapter, Horeczko T. "Acute Pain in Children". In Management of Pain and Procedural Sedation in Acute Care. Strayer R, Motov S, Nelson L (eds). 2017. Rather than the customary blog post summary, the full chapter (with links) is provided as a virtual reference. INTRODUCTION Pain is multifactorial: it is comprised of physical, psychological, emotional, cultural, and contextual features. In children often the predominant feature may not be initially apparent. Although clinicians may focus on the phys...
2017-01-0151 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookBronchiolitis"By the pricking of my thumbs, Something wheezing this way comes." -- Witches in Macbeth, with apologies to William Shakespeare "Bronchiolitis is like a pneumonia you can’t treat. We support, while the patient heals." -- Coach, still apologetic to the Bard The Who The U.S. definition is for children less than two years of age, while the European committee includes infants less than one year of age. This is important: toddlerhood brings with it other conditions that mimic bronchiolitis – the first-time wheeze in a toddler may be...
2016-12-0137 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPediatric Elbow InjuriesJohnny has fallen on an outstretched hand, and comes to you with a swollen, painful elbow. Position of comfort, analgesia, xrays, and now what? What am I seeing -- or not seeing -- here? First a refresher on radiographic anatomy of the elbow -- Images courtesy of Radioglypics (Open Access Radiology Education). Used with permission. Now that we have our adult anatomy reviewed, let's go through the development of the elbow in a child. We are all born with primary ossification centers -- the basic shapes of our l...
2016-11-0141 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookGI Bleeding in ChildrenBlood in the vomit. Blood in the stool. Blood in the diaper. How far do I go in my investigation? What do I really have to worry about? The differential diagnosis of GI bleeding in children is broad. (Here is the complete differential diagnosis) In the ED, we can simplify by categorizing by age and appearance. Neonates GI bleeding in the neonate (less than one month of age) is serious until proven otherwise. Well appearing? If this in obvious anal fissure, then no further work-up is necessary. Counsel on proper feeding and...
2016-10-0133 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPediatric Headache: Some Relief for AllSeemingly vague, but potentially dangerous... common, but possibly with consequences... ...or maybe just plain frustrating. Let's talk risk stratification, diagnosis, and management. Primary or Secondary? We can make headache as easy or as complicated as we like, but let's break it down to what we need to know now, and what the parents need to know when they go home. Primary headaches: headaches with no sinister secondary cause – like tension or migraine – are of course diagnoses of exclusion (cluster headache is exceedingly rare in children). Secondary headaches: headaches due to some underlying cause -- are what...
2016-09-0130 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookSubcutaneous RehydrationHave you ever been in any of these situations? ⇒ You have a stable child who just needs fluids, but no laboratory tests ⇒ You’ve tried PO hydration, to no avail, despite anti-emetics ⇒ You’re poking the stable, but dehydrated child repeatedly without success What now? Hypodermoclysis, otherwise known as subcutaneous rehydration. [Insert Player] Clysis comes from the same Greek word that “a flood” – hypodermoclysis refers to flooding the subcutaneous space with fluid, so that it can be absorbed systemically. Sound far-fetched? Well, it turns out, what is old is new again. In 1913, Dr Day first described th...
2016-08-0129 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookPlease STOP LIMPING!"She won't walk", or "He just looks like he's limping". So many things can be going on -- how do we tackle this chief complaint? You’re dreading a big work-up. You almost want to tell the kid – please, STOP LIMPING... STOP LIMPING! S – Septic Arthritis The most urgent part of our differential diagnosis. The hip is the most common joint affected, followed by the knee. Lab work can be helpful, as well as US of the hip to look for an effusion, but sometimes, regardless of the results, the joint just has to be tapped to know for s...
2016-07-0133 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookApproach to ShockDo we recognize shock early enough?
How do we prioritize our interventions?
How can we tell whether we’re making our patient better or worse?
World wide, shock is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children, mostly for failure to recognize or to treat adequately.
So, what is shock?
Simply put, shock is the inadequate delivery of oxygen to your tissues. That’s it. Our main focus is on improving our patient’s perfusion.
Oxygen delivery to the tissues depends on cardiac output, hemoglobin concentration, the oxygen saturation of the hemoglobin you have...
2016-06-0138 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookAltered Mental Status in ChildrenHow do you approach the child who may be altered?
Altered mental status in children can be subtle. Look for age-specific behaviors that range from irritability to anger to sleepiness to decreased interaction.
In the altered child, anchoring bias is your biggest enemy. Keep your mind open to the possibilities, and be ready to change it, when new information becomes available.
For altered adults, use AEIOU TIPS (Alcohol-Epilepsy-Insulin-Overdose-Uremia-Trauma-Infection-Psychosis-Stroke).
Try this for altered children: remember that they need their VITAMINS!
V – Vascular (e.g. arteriovenous malformation, systemic vasculitis)
I – In...
2016-05-0136 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookBig Labs, Little PeopleIt's a busy shift. Today no one seems to have a chief complaint.
Someone sends a troponin on a child. Good, bad, or ugly, how are you going to interpret the result?
And while we’re at it – what labs do I need to be careful with in children – sometimes the normal ranges of common labs can have our heads spinning!
Read on to go from bread-and-butter pediatric blood work to answer the question – what’s up with troponin, lactate, d-dimer, and BNP in kids?
A fundamental tenet of emergency medicine:
We balance our obligation to d...
2016-04-0131 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookMultisystem Trauma in Children, Part Two: Massive Transfusion, Trauma Imaging, and Resuscitative PearlsA 5-year-old boy was playing with his older brother in front of their home when he was struck by a car. He sustained a femur fracture, splenic laceration, and blunt head trauma – the so-called Waddell’s triad.
On arrival, he was in compensated shock, with tachycardia.
He decompensates and needs blood.
How do we manage his hemodynamics and when do we perform massive transfusion?
Pediatric Massive Transfusion
40 mL/kg of blood products given at any time within the first 24 hours.
Adolescents and Adult Massive Transfusion
6-8 units of packed red blood cells (PRBCs)
...
2016-03-0137 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookMultisystem Trauma in Children, Part One: Airway, Chest Tubes, and Resuscitative ThoracotomyTraumatized children need your full attention.
Protocols work well for adults, but trauma in children requires that we exercise our clinical muscles just a bit more.
Two main reasons:
Children have specific injury patterns
Their physiologic response to trauma is unique.
Crash course in pediatric anatomy and physiology in trauma
When you think of trauma in children, think of Charlie Brown. Large head, no neck, his chest and abdomen form an underdeveloped, amorphous shape.
Alternatively, think of children as apples – they are rounder than they are tall, with a large increased surface area. Apples don’t have a hard s...
2016-02-0135 min
EM BasicThe undifferentiated sick infant by Dr. Tim HoreczkoEM Basic is back with a re-broadcast from the awesome podcast Pediatric Emergency Playbook by Dr. Tim Horeczko. Tim is a double boarded in EM and Peds EM and works at Harbor-UCLA hospital. This was the first episode he published at the beginning of September and it is pure gold. Tim goes beyond the febrile neonate and talks about how to consider all possible causes for a sick infant- not just anchoring on sepsis the whole time! Tim presents a rational and systematic approach on how to deal with these young sick patients that get our anxiety and our adren...
2016-01-2500 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookVomiting in the Young Child: Nothing or NightmareIn the young child, vomiting is the great imitator:
Gastrointestinal, Neurologic, Metabolic, Respiratory, Renal, Infectious, Endocrine, Toxin-related, even Behavioral.
To help us organize, below is a review of can't-miss diagnoses by age.
The Neonate: Malrotation with Volvulus
In children with malrotation, 50% present within the first month of life, with the majority occurring in the first week after birth. 90% of children with malrotation with volvulus will present by one year of age. This is a pre-verbal child’s disease – which makes it even more of a challenge to recognize quickly.
The sequence of events usually is fussiness, irritability, and fo...
2016-01-0147 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookElectrical Injuries: Hertz So BadVictims of electrical injuries present either in extremis or as the seeming well patient with insidious, developing disease.
A targeted history usually gets you the information you need.
Four main things to find out:
1. Household or Industrial electricity?
Household electricity uses alternating current, or AC. Voltages across the world range anywhere from 100 to 240 V. Here in North America, most outlets and appliances use 120 volts, which is the measure of electrical tension, or the potential difference in electrical charge.
Cut-off between low voltage and high voltage is 1000 V.
Industrial energy may be AC or dire...
2015-12-0135 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookAdventures in RSIPediatric airway management is a skill that integrates the three types of knowledge as described by the ancient Greeks: episteme, or theoretical knowledge, techne, or technical knowledge, and phronesis, or practical wisdom, also called prudence.
Here we’ll invoke each type of knowledge and understanding as we go beyond the anatomical issues in pediatric airway management – to the advanced decision-making aspect of RSI and the what-to-do-when the rubber-hits-the road.
Case 1: Sepsis
Laura is a 2-month-old baby girl born at 32 weeks gestational age who today has been “breathing fast” per mother. On arrival she is in severe respiratory distress with nasal fla...
2015-11-0151 min
Pediatric Emergency PlaybookThe Technologically Dependent Child in the EDEMS is bringing you a child with a VP shunt, port-a-cath, trached on a vent, seizing, hypotensive, and now desaturating – ETA – 3 minutes. Are you ready?
Medicine is evolving. As technology advances, we need to meet the challenge of taking care of our patients who have come to rely on this technology for their basic needs. Before we go further, remember to assess the parent and the child as a unit. The caregiver who is usually the parent, is a rich source of knowledge about the child’s particular condition and past experience. Take them seriously, and be on the lookout f...
2015-10-0135 min